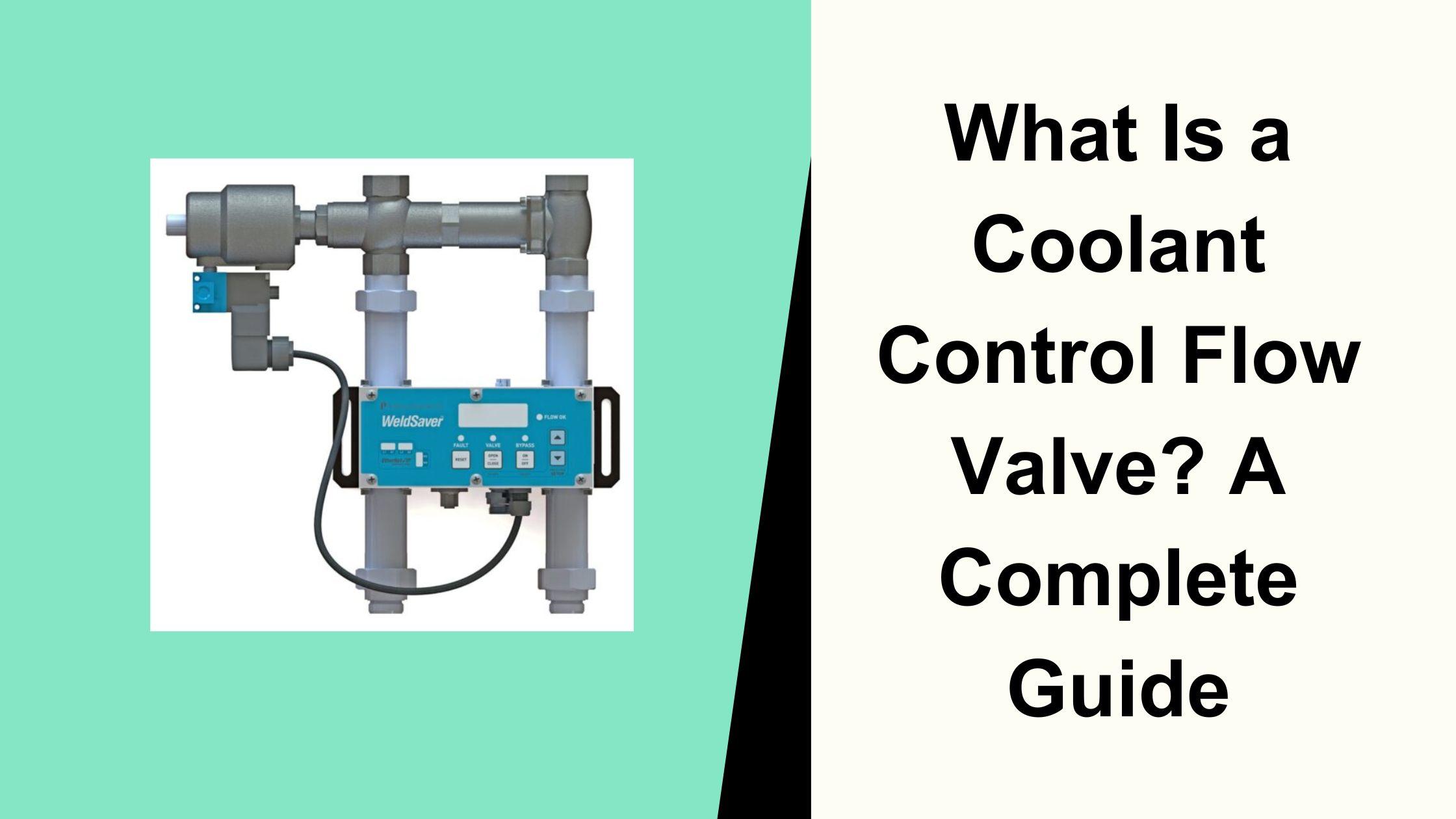
Coolant systems are crucial in regulating engine temperature in vehicles and machinery. Proper coolant flow prevents overheating and ensures optimal performance. One essential component in this system is the coolant control flow valve , which manages the coolant distribution based on engine demands. By controlling coolant flow, this valve helps maintain efficiency, prevent excessive wear, and improve fuel economy. Understanding the function, types, and maintenance of coolant control flow valves is vital for ensuring a well-functioning cooling system and preventing costly repairs. This article explores the key aspects of coolant control flow valves and their importance in vehicle and machinery cooling systems.
What Is a Coolant Control Flow Valve?
A coolant control flow valve is an element in a vehicle’s cooling system that regulates the flow of coolant to different parts of the engine and heater core. Its primary function is to ensure that coolant is directed efficiently to maintain optimal operating temperatures. This valve plays a crucial role in improving engine performance and preventing overheating. Controlling the coolant flow based on engine load and temperature helps maintain a stable thermal balance, ensuring smooth operation and enhanced longevity of the engine components.
How Does a Coolant Control Flow Valve Work?
The coolant control flow valve operates by opening and closing pathways for coolant circulation based on temperature sensors and engine demands. In mechanical models, a thermostat or vacuum actuator controls the valve. In electronic models, sensors communicate with the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust coolant flow dynamically. To optimize temperature management, the valve interacts with components such as the radiator, water pump, and thermostat. Regulating coolant flow ensures efficient cooling during high-load conditions and improves fuel economy by minimizing unnecessary coolant circulation when not needed.
Benefits of a Coolant Control Flow Valve
- Improved Engine Efficiency – Maintains optimal temperatures for efficient combustion and performance.
- Temperature Regulation – Prevents overheating and excessive cooling, ensuring stability.
- Fuel Economy and Emissions Reduction—Optimizing engine temperature reduces unnecessary coolant flow, improving fuel efficiency and lowering emissions.
Common Issues and Symptoms of a Failing Valve
- Overheating or Inconsistent Temperature Control – Malfunctioning valves can cause improper coolant flow, leading to temperature fluctuations.
- Check Engine Light Warnings – A failing valve may trigger fault codes related to the cooling system.
- Poor Heater Performance—If the valve is stuck closed or open, it can disrupt its core function, leading to inefficient cabin heating.
Maintenance and Replacement Tips
- Inspect for Faults – Regularly check for leaks, blockages, or signs of wear in the valve.
- Cleaning and Servicing – Clean the valve and surrounding components to prevent buildup and ensure smooth operation.
- When to Replace—If the valve shows significant wear, leaks, or operational failure, it must be replaced to maintain cooling system efficiency.
How to Choose the Right Coolant Control Flow Valve
Selecting the proper coolant control flow valve is crucial for ensuring efficient temperature regulation in various systems, including automotive engines, industrial machinery, and HVAC applications. The correct valve helps maintain optimal performance, prevents overheating, and ensures energy efficiency. Below are key elements to consider when choosing a coolant control flow valve, explained in detail.
1. Understand Your System Requirements
Before selecting a coolant control flow valve, it's essential to understand your system's specific requirements. Consider factors such as the type of coolant used, the temperature range, pressure conditions, and the flow rate needed. Reviewing the manufacturer's specifications and consulting an expert can help determine the best fit.
2. Consider the Valve Material
The valve's material is critical in its durability and compatibility with the coolant. Common materials include stainless steel, brass, and high-performance plastics. Stainless steel is positively resistant to corrosion and is ideal for harsh environments. Brass is cost-effective and works well with many coolant types but may not be suitable for highly corrosive fluids. High-performance plastics are lightweight and resistant to chemical reactions, making them ideal for specialized applications. Always check the coolant's chemical properties to ensure material compatibility.
3. Evaluate the Flow Control Mechanism
Different coolant control valves offer various flow control mechanisms, such as manual, electric, or pneumatic operation. Manual valves require human intervention for adjustments, making them suitable for applications requiring infrequent changes. Electrically controlled valves allow for automation and remote operation, enhancing efficiency in complex systems. Pneumatic valves use air pressure and are ideal for environments where electrical components might pose risks. Choosing the appropriate control mechanism ensures smooth and reliable operation.
4. Check Temperature and Pressure Ratings
Every coolant control flow valve is designed to operate within specific temperature and pressure limits. Selecting a valve with a lower rating than required can lead to failures, leaks, or reduced efficiency. Ensure the valve can withstand your system's maximum operating temperature and pressure. Reviewing the manufacturer's datasheet will provide insights into these ratings and help you make an informed decision.
Conclusion
A properly functioning coolant control flow valve is essential for engine efficiency, temperature stability, and fuel economy. Regular inspection and timely replacement of a faulty valve can prevent overheating issues and costly engine damage. Understanding the different types of valves and their functions helps vehicle owners make informed decisions when selecting a replacement. By maintaining the cooling system, drivers can enhance vehicle performance, reduce emissions, and prolong engine lifespan.
FAQs
- What happens if my coolant control flow valve fails?
- A failing valve can lead to overheating, poor heater performance, and increased fuel consumption.
- How often should I inspect my coolant control flow valve?
- It should be checked during routine maintenance or at least every 30,000 miles.
- Can I replace the coolant control flow valve myself?
- Yes, with basic mechanical knowledge and tools, but professional installation ensures proper function.
- Are electronic coolant control valves better than mechanical ones?
- Electronic valves offer more precise control but may be more expensive to replace.
- Does a coolant control flow valve affect fuel efficiency?
- Yes, optimizing temperature regulation contributes to better fuel economy and reduced emissions.