Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is an evidence-based approach increasingly used to treat anxiety and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). It helps individuals manage intrusive thoughts and compulsions by promoting acceptance, mindfulness, and values-driven action rather than trying to eliminate symptoms directly. ACT enables people to respond to distressing thoughts in healthier ways, reducing their impact and improving overall well-being.
Online therapy options have made ACT more accessible, allowing those with anxiety or OCD to connect with specialized therapists from anywhere. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for individuals who face barriers to in-person treatment or prefer virtual sessions. Many therapists now offer tailored ACT sessions that focus on helping clients accept difficult feelings and commit to positive behavioral changes.
The use of ACT for anxiety and OCD aligns well with the challenges these conditions present, as it addresses not only symptoms but the relationship to thoughts and emotions. With online ACT therapy becoming more recognized, people have practical, effective support available to navigate their mental health challenges in a convenient and supportive environment.
ACT Therapy for Anxiety and OCD
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) targets how individuals relate to their thoughts and feelings rather than trying to eliminate symptoms directly. ACT Therapy for Anxiety emphasizes psychological flexibility, mindfulness, and committed action based on personal values to reduce distress from anxiety and OCD.
Core Principles of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
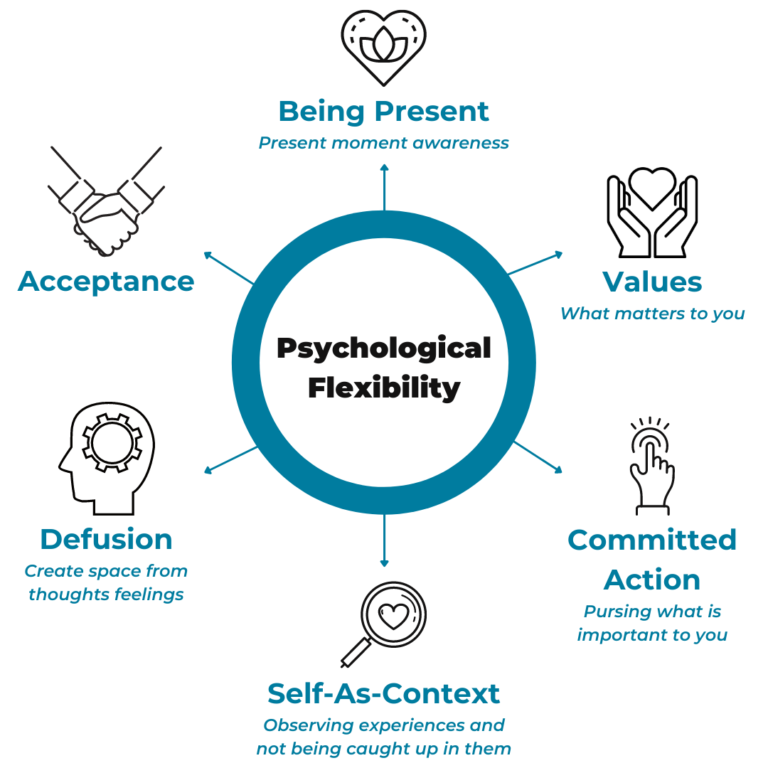
ACT is grounded in six core processes: acceptance, cognitive defusion, being present, self-as-context, values, and committed action. Acceptance involves allowing unpleasant thoughts and emotions to exist without trying to control or avoid them. Cognitive defusion helps individuals observe thoughts without attachment or judgment.
Mindfulness encourages staying in the present moment and noticing experiences objectively. The self-as-context process refers to observing oneself as distinct from one’s thoughts. ACT places strong emphasis on clarifying values and engaging in committed behaviors aligned with those values, promoting meaningful life engagement despite symptoms.
Benefits for Treating Anxiety and OCD
ACT helps reduce the struggle against intrusive thoughts common in anxiety and OCD by changing how individuals respond to them. It teaches clients to accept distressing thoughts rather than engage in compulsive behaviors or avoidance, which can reinforce anxiety.
Clients often report increased psychological flexibility, enabling them to live in alignment with their values even while experiencing symptoms. This approach can reduce overall distress and improve quality of life. ACT’s mindfulness focus improves awareness and emotion regulation, critical in managing anxiety and OCD symptom cycles.
ACT vs. Traditional Anxiety Treatments
Traditional anxiety and OCD treatments often focus on symptom reduction through exposure or medication. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), especially Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP), is considered the first-line treatment for OCD due to strong evidence supporting its symptom reduction effectiveness.
ACT differs by prioritizing acceptance of symptoms and values-guided action over direct symptom change. While ACT is newer and has less extensive research compared to ERP, it can be combined with traditional methods or used when clients struggle with resistance to exposure or symptom control techniques. ACT’s emphasis on mindfulness and acceptance offers an alternative pathway to reducing distress related to anxiety and OCD.
Choosing an Online OCD Therapist
Selecting the right online therapist for OCD involves verifying their expertise in Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) and understanding how therapy platforms operate. Being prepared for virtual sessions enhances the effectiveness of treatment and comfort during the process.
Finding Qualified ACT-Based Therapists Online
Not all therapists specialize in ACT for OCD, so it's important to confirm their qualifications. Look for licensed professionals who have specific training in ACT, as well as experience treating OCD.
Therapists who combine ACT with exposure and response prevention (ERP) therapy may offer a more comprehensive approach. Checking credentials on professional directories or therapy platforms can provide verification.
Patient reviews and therapist backgrounds help assess their ability to manage OCD symptoms effectively. Prioritize therapists who engage in continuing education related to OCD and ACT to ensure up-to-date treatment methods.
Evaluating Online Therapy Platforms
Different platforms vary in therapist selection, insurance acceptance, and access to medication management. Some services, like NOCD, focus exclusively on OCD with therapists trained in evidence-based treatments.
Look for platforms that offer detailed therapist bios, credential verification, and clear pricing. Insurance support and flexible session scheduling also improve accessibility.
Consider whether the platform enables in-session coaching for exposure exercises, as this is critical for OCD therapy. User experience, privacy policies, and customer support should factor into the choice.
| Factor | What to Check |
| Therapist Specialization | ACT expertise and OCD treatment focus |
| Insurance Support | Accepted insurance plans |
| Session Flexibility | Appointment availability and format |
| Medication Management | Access to prescribing professionals |
Preparing for Your First Virtual Session
Before the initial session, test your internet connection and ensure privacy to create a distraction-free environment. Familiarize yourself with the platform's interface ahead of time.
Have a list of your OCD symptoms and goals ready to discuss. Sharing your experience with anxiety and compulsions helps the therapist tailor the ACT approach effectively.
Be ready to engage in exposure or mindfulness exercises during the session. Early openness to these strategies maximizes treatment progress from the start.